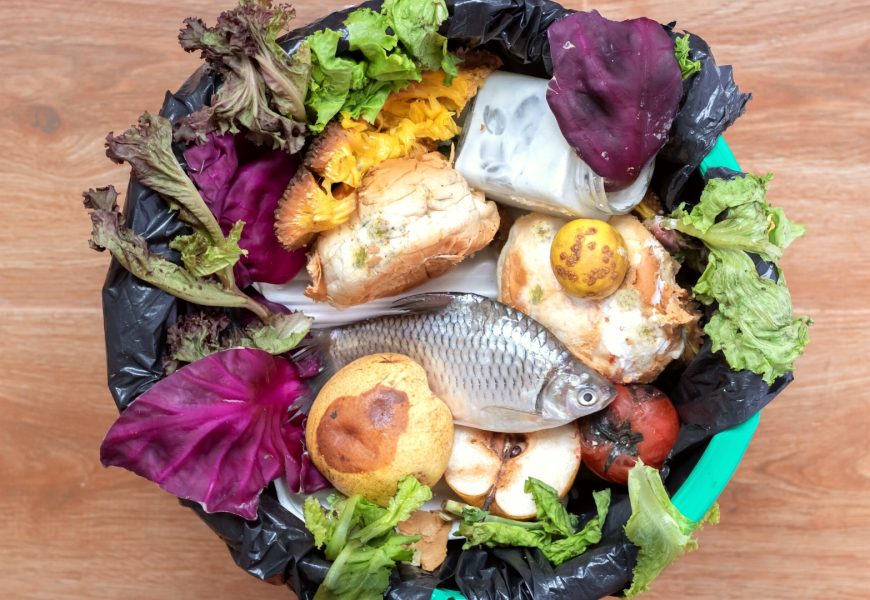
The kitchen, a bustling hub of activity, is also a significant generator of waste. From food scraps to packaging materials, the impact of kitchen waste on the environment is substantial. However, with conscious efforts and effective waste management systems, individuals can minimize their environmental footprint. In this article, we will explore strategies to optimize kitchen waste management systems, aiming for minimal environmental impact and contributing to a more sustainable and eco-friendly lifestyle.
1. Embrace the Three Rs: Reduce, Reuse, Recycle
a. Reduce:
- Mindful Shopping: Plan meals, create shopping lists, and buy only what is needed to reduce food waste.
- Bulk Buying: Purchase items in bulk to minimize packaging waste and reduce the need for frequent trips to the store.
- Choose Sustainable Packaging: Opt for products with minimal or eco-friendly packaging to reduce overall waste.
b. Reuse:
- Reusable Containers: Use reusable containers for food storage instead of single-use plastic bags or wraps.
- Repurpose Food Scraps: Repurpose vegetable peels and scraps for homemade broths or compost.
c. Recycle:
- Separate Waste Streams: Set up a recycling station in the kitchen with clearly marked bins for paper, plastic, glass, and metal.
- Check Local Recycling Guidelines: Stay informed about local recycling guidelines to ensure proper disposal of recyclable materials.
2. Implement a Comprehensive Composting System
a. Benefits of Composting:
- Reduced Methane Emissions: Composting organic waste prevents it from ending up in landfills, where it would produce methane, a potent greenhouse gas.
- Nutrient-Rich Soil Amendment: The resulting compost enriches soil, improving its structure and fertility.
b. Composting Tips:
- Set Up a Compost Bin: Use a designated compost bin for fruit and vegetable scraps, coffee grounds, eggshells, and yard waste.
- Balance Green and Brown Materials: Maintain a balance between nitrogen-rich “green” materials (food scraps) and carbon-rich “brown” materials (leaves, paper) for optimal composting.
3. Utilize Food Waste Reduction Techniques
a. Meal Planning:
- Plan and Prep Meals: Plan meals in advance to minimize overbuying and reduce the likelihood of unused perishables.
- Leftover Makeovers: Get creative with leftovers by transforming them into new dishes to prevent food waste.
b. Smart Storage Practices:
- First In, First Out (FIFO): Organize the refrigerator and pantry to prioritize using older items first to prevent expiration and waste.
- Proper Storage: Store fruits and vegetables properly to extend their freshness and prevent premature spoilage.
4. Invest in Smart Appliances for Reduced Energy Consumption
a. Energy-Efficient Appliances:
- Energy Star Ratings: Choose kitchen appliances with Energy Star ratings to ensure they meet energy efficiency standards.
- Optimize Refrigerator Settings: Set refrigerators and freezers at recommended temperatures to minimize energy consumption.
b. Smart Technology Integration:
- Remote Monitoring: Some smart appliances allow remote monitoring and control, enabling users to adjust settings for optimal energy efficiency.
- Adaptive Features: Appliances with adaptive features can adjust operation based on usage patterns, optimizing energy consumption.
5. Promote Sustainable Waste Disposal Methods
a. Proper Disposal of Hazardous Materials:
- Safe Disposal Practices: Dispose of hazardous materials like cleaning agents, batteries, and light bulbs through designated disposal programs to prevent environmental contamination.
- Explore Recycling Programs: Investigate local programs for the proper disposal of electronic waste (e-waste).
b. Responsible Disposal of Non-Recyclables:
- Landfill Diversion: Explore alternative waste disposal methods, such as waste-to-energy facilities, to divert waste from landfills.
- Check for Local Disposal Options: Research local facilities that accept non-recyclable items for responsible disposal.
6. Educate and Involve Household Members
a. Shared Responsibility:
- Educational Initiatives: Conduct educational sessions to raise awareness about the environmental impact of kitchen waste.
- Involve Family Members: Encourage active participation from all household members in waste reduction and recycling efforts.
b. Reward Systems:
- Positive Reinforcement: Implement a reward system to motivate household members to actively engage in sustainable waste management practices.
- Celebrate Achievements: Acknowledge milestones in waste reduction and recycling to reinforce positive habits.
7. Optimize Water Usage in Kitchen Cleaning
a. Conscious Water Practices:
- Water-Efficient Faucets: Install water-efficient faucets to minimize water usage during dishwashing and cleaning.
- Capture and Reuse Greywater: Capture and reuse greywater (lightly used water) for tasks like watering plants or cleaning.
b. Efficient Dishwashing:
- Full Load Operation: Run the dishwasher only when it is fully loaded to maximize efficiency and reduce water usage.
- Eco-Friendly Detergents: Choose eco-friendly dishwasher detergents to minimize environmental impact.
8. Explore Packaging Alternatives and Eco-Friendly Products
a. Reducing Packaging Waste:
- Bulk Purchases: Buy in bulk to reduce packaging waste and opt for products with minimal or sustainable packaging.
- Eco-Friendly Packaging: Choose products packaged in materials that are recyclable or biodegradable.
b. DIY Cleaning Solutions:
- Homemade Cleaners: Make DIY cleaning solutions using common household ingredients to reduce reliance on commercial cleaners with potentially harmful chemicals.
- Reusable Cleaning Tools: Use reusable cleaning cloths and brushes instead of disposable alternatives.
9. Engage in Community Initiatives and Recycling Programs
a. Community Recycling Programs:
- Participate in Local Programs: Join community initiatives and recycling programs to enhance waste management efforts at a broader level.
- Support Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR): Advocate for EPR policies that hold manufacturers accountable for the life cycle of their products.
b. Sharing and Donating:
- Community Sharing Initiatives: Participate in community-sharing initiatives to exchange unused or surplus food items.
- Donate Surplus Non-Perishables: Donate non-perishable food items to local food banks or community organizations.
Conclusion:
Optimizing kitchen waste management systems for minimal environmental impact involves a multifaceted approach, from reducing waste at the source to responsible disposal methods. By embracing the three Rs, implementing composting systems, and utilizing food waste reduction techniques, individuals can significantly minimize their kitchen’s environmental footprint. Additionally, the integration of smart appliances, sustainable waste disposal methods, and the use of eco-friendly products contribute to a more eco-conscious kitchen. Through education, involvement, and community initiatives, individuals can collectively work towards creating a kitchen environment that aligns with principles of sustainability and environmental stewardship.