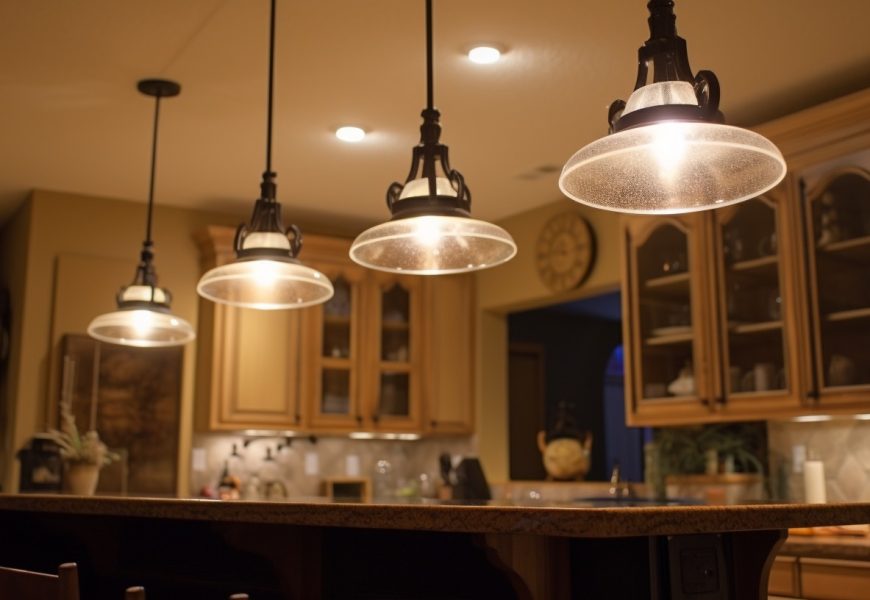
The kitchen, often considered the heart of the home, is a space where functionality and aesthetics converge. As individuals seek to create sustainable living environments, the choices made in lighting play a crucial role in minimizing environmental impact. This article explores the environmental considerations involved in choosing kitchen lighting options, shedding light on energy efficiency, material choices, and the overall impact on the planet.
1. Energy-Efficient Lighting Solutions:
a. LED Lighting:
One of the most energy-efficient lighting options available today is Light Emitting Diode (LED) lighting. LEDs consume significantly less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs, translating to reduced electricity bills and a lower overall environmental footprint.
b. Longevity and Durability:
LEDs have an impressive lifespan, often lasting tens of thousands of hours. Their durability reduces the frequency of replacements, minimizing the production of electronic waste associated with disposable bulbs.
c. Instant Light Output:
Unlike some other energy-efficient options, LEDs provide instant illumination without the delay that can occur with certain compact fluorescent lights (CFLs). This feature contributes to both energy efficiency and user convenience.
2. Natural Light Integration:
a. Maximizing Daylight:
Integrating natural light into the kitchen design is a sustainable practice that not only reduces the need for artificial lighting during the day but also positively impacts mood and well-being.
b. Strategic Window Placement:
Architectural considerations, such as strategically placing windows or skylights, can optimize natural light. This reduces the reliance on artificial lighting and promotes a healthier indoor environment.
3. Smart Lighting Controls:
a. Dimmers and Sensors:
Installing dimmer switches and motion sensors allows for precise control over the amount of light emitted and when it is needed. This not only contributes to energy savings but also extends the lifespan of light bulbs.
b. Home Automation Systems:
Smart lighting systems that can be integrated into home automation platforms enable users to schedule lighting based on daily routines or adjust settings remotely. This level of control enhances energy efficiency and reduces unnecessary usage.
4. Recyclable and Sustainable Materials:
a. Material Selection for Fixtures:
When choosing lighting fixtures, consider those made from recyclable or sustainable materials. Options like bamboo, recycled glass, or responsibly sourced wood contribute to a more eco-friendly choice.
b. Recyclable Packaging:
Mindful choices extend beyond the product itself to its packaging. Opt for lighting products that use minimal and recyclable packaging, reducing the overall environmental impact associated with disposal.
5. Energy Star Certification:
a. Energy Star-Qualified Fixtures:
Energy Star-certified lighting fixtures meet strict energy efficiency and performance standards set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Choosing Energy Star-qualified options ensures that the fixtures adhere to environmentally responsible practices.
b. Energy Star Bulbs:
Similarly, Energy Star-rated light bulbs, including LEDs and CFLs, are designed to consume less energy and meet specific performance criteria. These bulbs contribute to energy savings and align with sustainability goals.
6. Low-Voltage Lighting Systems:
a. Reduced Energy Consumption:
Low-voltage lighting systems, such as LED strip lights or puck lights, consume less energy than their high-voltage counterparts. This can be particularly beneficial for accent lighting or under-cabinet illumination.
b. Enhanced Safety:
Lower voltage systems are generally safer, reducing the risk of electrical shocks. This consideration aligns with a commitment to both environmental and user safety.
7. Minimalist Design and Compact Fixtures:
a. Reduced Material Usage:
Choosing compact and minimalist lighting fixtures not only contributes to a modern aesthetic but also reduces the overall material usage in production. This aligns with the principles of sustainable design and manufacturing.
b. Lighting Efficiency:
Compact fixtures often utilize advanced lighting technologies, ensuring efficiency in light distribution. This can result in less energy waste and improved illumination where it is needed.
8. Proper Disposal of Old Lighting Fixtures:
a. Recycling Options:
When replacing old lighting fixtures, explore recycling options for the disposed items. Many local recycling centers accept various types of lighting components, including bulbs and fixtures.
b. Hazardous Material Awareness:
Certain lighting technologies, such as CFLs, contain small amounts of mercury. Proper disposal ensures that hazardous materials are handled responsibly, preventing environmental contamination.
9. Consideration of Light Color Temperature:
a. Warm vs. Cool Light:
Understanding the color temperature of light is essential for creating the desired ambiance in the kitchen. While personal preference plays a role, warmer color temperatures (measured in Kelvins) often contribute to a cozier atmosphere.
b. LED Color Temperature Options:
LEDs come in a range of color temperatures, allowing users to choose lighting that aligns with their preferences and the intended mood. This versatility enhances the overall user experience.
10. Localized Task Lighting:
a. Focused Illumination:
Implementing task lighting in specific kitchen areas, such as over the stove or sink, provides focused illumination where it is needed. This targeted approach reduces the need for overall ambient lighting, promoting energy efficiency.
b. Task Lighting Placement:
Strategic placement of task lighting ensures that work surfaces are well-lit without the need for excessive ambient lighting. This approach optimizes energy consumption while enhancing functionality.
Conclusion:
Choosing environmentally conscious lighting options for the kitchen is a step towards a greener and more sustainable home. From energy-efficient technologies like LEDs to considerations of materials, disposal practices, and the integration of natural light, there are numerous ways individuals can minimize the environmental impact of their lighting choices. As awareness of sustainable living practices grows, incorporating eco-friendly lighting into kitchen design becomes not only a responsible choice but also an opportunity to create a well-lit, aesthetically pleasing, and environmentally mindful space. By illuminating our homes with consideration for the planet, we can all contribute to a brighter, more sustainable future.