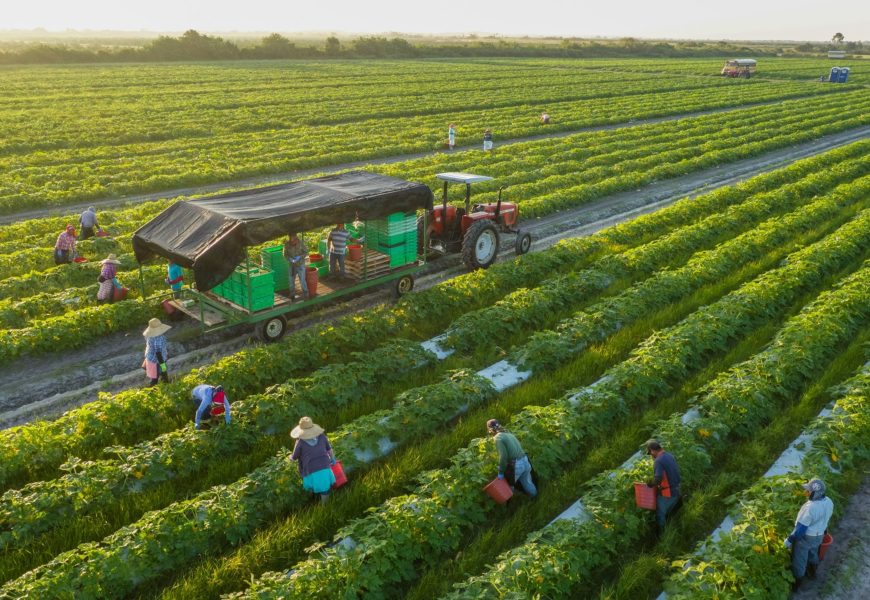
In a world where environmental consciousness is at the forefront of many minds, the choice to embrace a green and sustainable lifestyle extends beyond daily habits to the very roots of our food systems. Organic farming, with its commitment to ecological balance, soil health, and minimized chemical inputs, plays a pivotal role in promoting sustainability. In this article, we explore the multifaceted contributions of organic farming to a green lifestyle and its positive impact on the environment, human health, and the planet’s overall well-being.
1. Preservation of Soil Health:
Organic farming prioritizes soil health as a foundational element of sustainable agriculture. Unlike conventional farming that relies heavily on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, organic practices focus on enhancing soil fertility through natural means. Cover cropping, crop rotation, and composting are integral to organic farming, fostering soil structure, moisture retention, and the overall health of the terrestrial ecosystem.
2. Reduction of Chemical Inputs:
One of the defining features of organic farming is the strict limitation on synthetic chemicals. Conventional agriculture often involves the widespread use of pesticides and herbicides, contributing to soil contamination, water pollution, and the loss of biodiversity. By minimizing chemical inputs, organic farming protects ecosystems, aquatic habitats, and the broader environment from the adverse effects of agrochemicals.
3. Promotion of Biodiversity:
Organic farms typically embrace diverse crop rotations and intercropping strategies, which contribute to the preservation of biodiversity. Unlike monoculture practices common in conventional agriculture, organic farms create habitats that support a variety of plant and animal species. This diversity enhances natural pest control, reduces the risk of crop diseases, and fosters a resilient and balanced ecosystem.
4. Conservation of Water Resources:
The emphasis on soil health and water conservation is integral to organic farming. Practices such as mulching and cover cropping reduce water evaporation from the soil, enhancing water retention. Additionally, organic farms often employ efficient irrigation systems that minimize water wastage, contributing to responsible water management in agriculture.
5. Mitigation of Greenhouse Gas Emissions:
Conventional farming practices, particularly in industrialized agriculture, contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. The production and use of synthetic fertilizers, as well as the management of large-scale livestock operations, release substantial amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Organic farming, with its focus on natural soil enrichment and reduced dependence on fossil fuels, helps mitigate these emissions.
6. Promotion of Sustainable Crop Rotation:
Crop rotation is a key practice in organic farming that promotes soil fertility and pest control. By diversifying crops in a systematic rotation, organic farmers reduce the risk of soil degradation and nutrient depletion. This sustainable approach contributes to the long-term health and productivity of the land.
7. Support for Small-Scale and Local Agriculture:
Organic farming often aligns with principles of small-scale and local agriculture. Supporting local farmers reduces the carbon footprint associated with the transportation of food over long distances. It fosters community resilience, promotes regional biodiversity, and creates a more sustainable and interconnected food system.
8. Protection of Pollinators:
The decline of pollinator populations, such as bees and butterflies, poses a significant threat to global food production. Organic farming, with its reduced use of synthetic pesticides, provides a safer environment for pollinators. By avoiding the harmful impacts of neonicotinoids and other pesticides, organic farms contribute to the protection of essential pollinator species.
9. Promotion of Regenerative Agriculture:
Regenerative agriculture, a holistic approach to farming that aims to enhance ecosystem health, is closely aligned with organic farming principles. Both emphasize the importance of soil health, biodiversity, and sustainable practices. By adopting regenerative techniques, organic farmers contribute to the restoration of ecosystems and the creation of resilient agricultural systems.
10. Improved Nutritional Quality of Food:
Studies suggest that organic crops often contain higher levels of certain nutrients and antioxidants compared to conventionally grown counterparts. By avoiding synthetic pesticides and chemical fertilizers, organic farming supports the production of nutrient-dense crops, contributing to the overall health and well-being of individuals consuming organic produce.
In conclusion, organic farming emerges as a cornerstone of promoting a green and sustainable lifestyle. Its commitment to soil health, biodiversity, and reduced chemical inputs aligns with the principles necessary for a resilient and ecologically responsible agricultural system. As individuals increasingly recognize the interconnectedness of their choices with the health of the planet, supporting organic farming practices becomes not just an agricultural preference but a conscious step towards fostering a more sustainable and harmonious relationship between humanity and the environment.